Error Handling and Debugging
- What is error handling and debugging? Errors, bugs, and therefore debugging are a part of life for a programmer. … Dealing with errors actually involves two very different processes: error handling and debugging. Error handling is a combination of coding and methodology that allows your program to anticipate user and other errors.

- The greeting variable gets its value from the greetUser() function.
- greetUser() creates the message by combining the string ‘He 11 o ‘ with the result of getName ().
- getName () returns the name to greetUser().
- greetUser() now knows the name, and combines it with the string. It then returns the message to the statement that called it in step 1.
- This greeting variable is written to an alert box.
- execution contexts: is defined as the environment in which the JavaScript code is executed. By environment, I mean the value of this , variables, objects, and functions JavaScript code has access to at a particular time.
Variable Scop :scope is function-based while context is object-based. In other words, scope pertains to the variable access of a function when it is invoked and is unique to each invocation. Context is always the value of the this keyword, which is a reference to the object that “owns” the currently executing code.
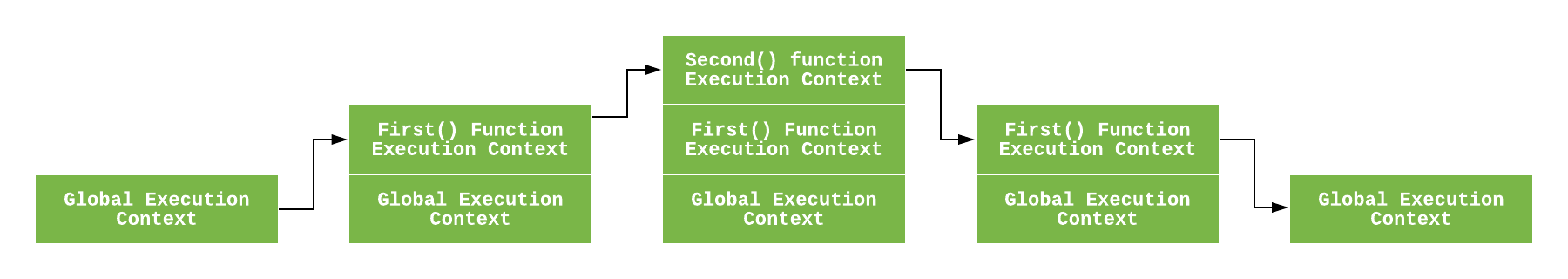
- Stack
- ERROR OBJECTS
Browser support: Represents a run-time error caused by a script operation. JavaScript interpreters throw an Error object, when a script error (exception) occurs. In some cases when the error is caused by a DOM operation, JavaScript interpreters throw an DOMException object, not an Error object.

-
HOW TO DEAL WITH ERRORS
- A try-catch-finally statement is a code or program that handles exceptions.
- The try clause runs the code that generates exceptions.
- The catch clause catches exceptions that are thrown.
- A finally clause always gets executed.
- The throw statement generates exceptions.
- DEBUGGING TIPS
- Outputting JavaScript debugging messages to the browser. One of the easiest ways to debug JavaScript has always been to output data to the browser. …
- Popping up messages with
alert()… - Logging lines to console with
console.log()… - Pausing code execution with the
debugger…
- common errors
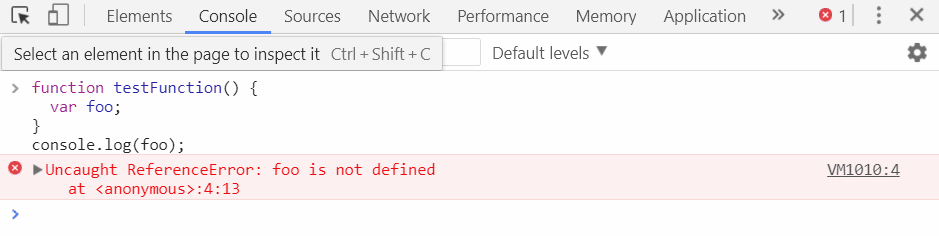 1. Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property. …
2. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not an object (evaluating. …
3. TypeError: null is not an object (evaluating. …
4. (unknown): Script error. …
5. TypeError: Object doesn’t support property. …
6. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not a function.
1. Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property. …
2. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not an object (evaluating. …
3. TypeError: null is not an object (evaluating. …
4. (unknown): Script error. …
5. TypeError: Object doesn’t support property. …
6. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not a function.