- Forms
HTML form is a section of a document containing normal content, markup, special elements called controls (checkboxes, radio buttons, menus, etc.), and labels on those controls. Users generally “complete” a form by modifying its controls (entering text, selecting menu items, etc.), before submitting the form to an agent for processing (e.g., to a Web server, to a mail server, etc.)
- How Forms Work?
- Your visitor loads the form page in her web browser.
-
Your visitor fills the form and submits it
-
The form submission data is sent to the web server
-
The web server processes the request
-
A response is sent back to the browser
-
Controls:Users interact with forms through named controls.
-
buttons: Authors may create three types of buttons:
submit buttons: When activated, a submit button submits a form. A form may contain more than one submit button. reset buttons: When activated, a reset button resets all controls to their initial values. push buttons: Push buttons have no default behavior. Each push button may have client-side scripts associated with the element's event attributes. When an event occurs (e.g., the user presses the button, releases it, etc.), the associated script is triggered. Authors should specify the scripting language of a push button script through a default script declaration (with the META element).Authors create buttons with the BUTTON element or the INPUT element. Please consult the definitions of these elements for details about specifying different button types.
-
checkboxes Checkboxes (and radio buttons) are on/off switches that may be toggled by the user. A switch is “on” when the control element’s checked attribute is set. When a form is submitted, only “on” checkbox controls can become successful.
Several checkboxes in a form may share the same control name. Thus, for example, checkboxes allow users to select several values for the same property. The INPUT element is used to create a checkbox control.
-
radio buttons Radio buttons are like checkboxes except that when several share the same control name, they are mutually exclusive: when one is switched “on”, all others with the same name are switched “off”. The INPUT element is used to create a radio button control. If no radio button in a set sharing the same control name is initially “on”, user agent behavior for choosing which control is initially “on” is undefined. Note. Since existing implementations handle this case differently, the current specification differs from RFC 1866 ([RFC1866] section 8.1.2.4), which states:
At all times, exactly one of the radio buttons in a set is checked. If none of the <INPUT> elements of a set of radio buttons specifies `CHECKED', then the user agent must check the first radio button of the set initially.Since user agent behavior differs, authors should ensure that in each set of radio buttons that one is initially “on”.
- menus Menus offer users options from which to choose. The SELECT element creates a menu, in combination with the OPTGROUP and OPTION elements.
- text input Authors may create two types of controls that allow users to input text. The INPUT element creates a single-line input control and the TEXTAREA element creates a multi-line input control. In both cases, the input text becomes the control’s current value.
- file select This control type allows the user to select files so that their contents may be submitted with a form. The INPUT element is used to create a file select control.
- hidden controls Authors may create controls that are not rendered but whose values are submitted with a form. Authors generally use this control type to store information between client/server exchanges that would otherwise be lost due to the stateless nature of HTTP (see [RFC2616]). The INPUT element is used to create a hidden control.
- object controls Authors may insert generic objects in forms such that associated values are submitted along with other controls. Authors create object controls with the OBJECT element.
The elements used to create controls generally appear inside a FORM element, but may also appear outside of a FORM element declaration when they are used to build user interfaces. This is discussed in the section on intrinsic events. Note that controls outside a form cannot be successful controls.

- list-style:

- Styling Forms this link define how the wep devloper can dtyleing his form by css
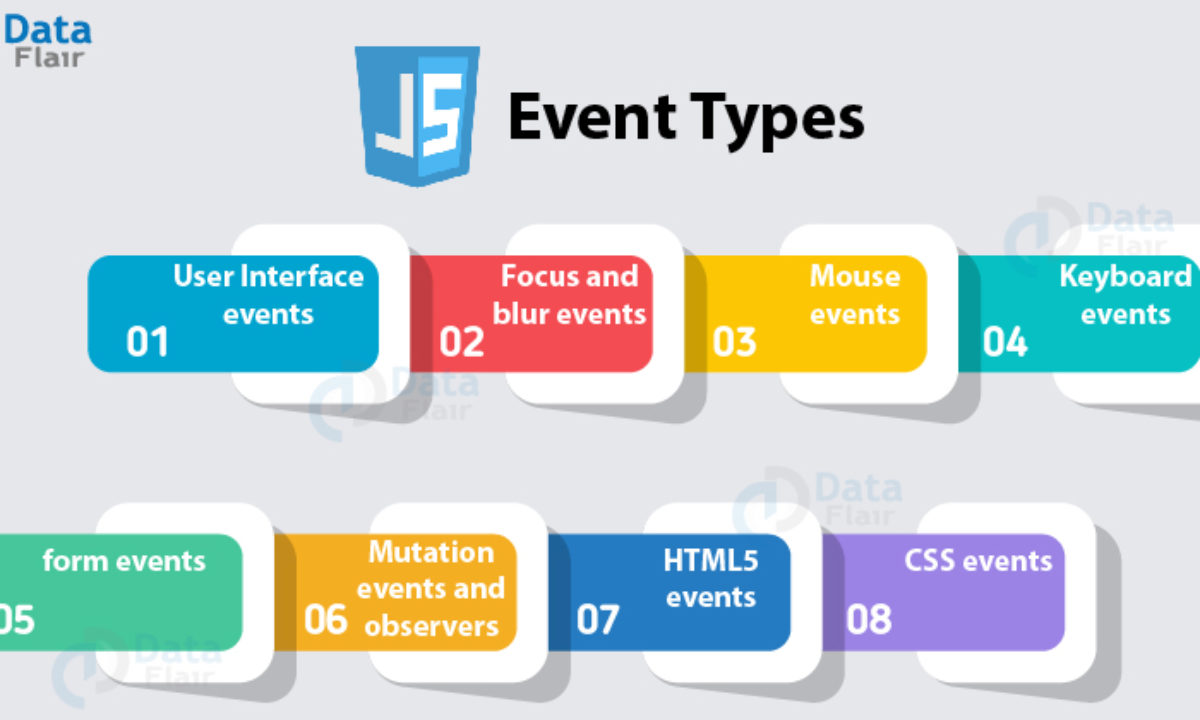
Events JS
- What is an Event ? JavaScript’s interaction with HTML is handled through events that occur when the user or the browser manipulates a page.
When the page loads, it is called an event. When the user clicks a button, that click too is an event. Other examples include events like pressing any key, closing a window, resizing a window, etc.
Developers can use these events to execute JavaScript coded responses, which cause buttons to close windows, messages to be displayed to users, data to be validated, and virtually any other type of response imaginable.
Events are a part of the Document Object Model (DOM) Level 3 and every HTML element contains a set of events which can trigger JavaScript Code.

- eventlistener :

- EVENT DELEGATION

- Mouse event element :
